Large Language Models (LLMs) work by learning patterns from massive amounts of text and using those patterns to predict the next word in a sentence. They don’t “think” or “understand” like humans – they recognize statistical relationships between words, concepts, and structures to generate meaningful and context-aware responses.
This simple idea of prediction – powered by billions of parameters, deep neural networks, and transformer architecture – is what allows LLMs to write essays, explain code, create content, analyze data, hold conversations, and more. Now let’s explore the full breakdown of how these models truly work under the hood.
What Is a Large Language Model (LLM)?
A Large Language Model (LLM) is an advanced form of artificial intelligence designed to read, understand, and generate human-like language. It learns this capability by analyzing massive amounts of text—ranging from books and research papers to websites, conversations, and code. Through this exposure, the model begins to recognize patterns in grammar, meaning, tone, and context, enabling it to respond intelligently across many different tasks.
Modern LLMs such as GPT-5, Claude, Llama, and Gemini are capable of performing a wide variety of language-based functions. They don’t simply repeat information; they interpret context, understand user intent, and produce responses that feel coherent and helpful.
What Can LLMs Do?
LLMs are powerful because they can:
- Answer complex questions
- Generate text, long-form content, and even working code
- Understand meaning, tone, and contextual clues
- Translate languages with high accuracy
- Reason and draw inferences from patterns
- Summarize lengthy documents or datasets
- Engage in smooth, natural conversation
These capabilities make LLMs useful in education, business, programming, healthcare, creative work, and countless other fields.
The strength of LLMs comes from the architecture they are built on – the Transformer. This revolutionary design changed the AI industry by enabling models to understand long sequences of text and identify relationships between words, even when those words appear far apart. Because of this, LLMs can capture deeper meaning, maintain context, and generate responses that feel logical and human-like.
How LLMs Learn: Training Explained Simply
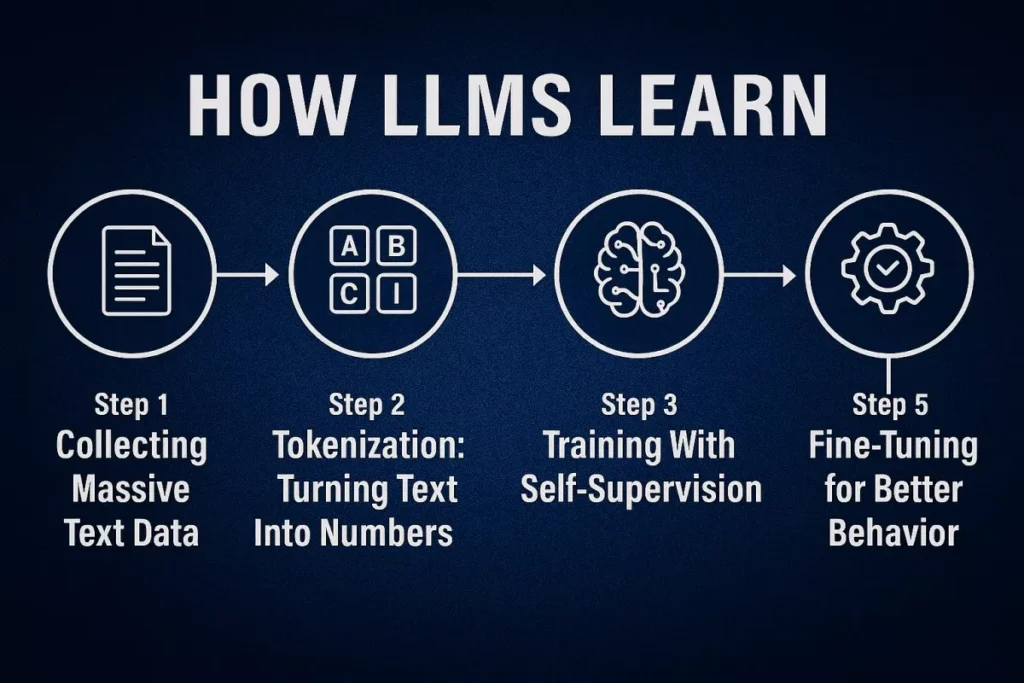
The training process is what transforms a Large Language Model from an empty neural network into a system capable of writing, reasoning, summarizing, and understanding complex language. LLMs don’t start with knowledge – they learn everything from the data they are exposed to. Through several stages of training, the model gradually becomes more intelligent, accurate, and conversational.
Step 1 – Collecting Massive Text Data
The first step in training an LLM is gathering a huge variety of text from across the internet and other sources. This is necessary because the more diverse the data, the more the model learns about grammar, tone, structure, and the world itself.
LLMs are typically trained on:
- Books and academic papers
- News articles and blogs
- Websites and public forums
- Technical documentation
- Social media conversations
- Code repositories
- Public datasets and curated corpora
This enormous dataset gives the model exposure to different writing styles, subjects, languages, and reasoning patterns. As a result, it begins to recognize how humans communicate in countless contexts—from casual chats to scientific research.
Step 2 – Tokenization: Turning Text Into Numbers
Although LLMs appear to understand language, they can only process numbers. That means every piece of text must be converted into numerical units called tokens.
Tokens can represent:
- Entire words
- Parts of words
- Characters
- Punctuation
- Special symbols
Example:
“Language models are amazing” → [“Language”, “models”, “are”, “amazing”]
Once text is tokenized, each token becomes a numerical vector—a mathematical representation the model can learn from. Tokenization allows the model to break down huge amounts of text into smaller, understandable components.
Step 3 – Training With Self-Supervision
LLMs learn using a method called self-supervised learning, which means the model learns directly from the data itself—without human labeling.
The idea is simple:
- The model predicts the next word or missing word
- If it is wrong, it learns from the mistake
- If it’s right, it strengthens that understanding
Example training prompt:
“The cat is sitting on the __.”
Model prediction:
- “table” → Correct → Reinforced
- “roof” → Incorrect → Adjust
By repeating this process billions (or even trillions) of times, the model gradually develops an understanding of:
- Grammar and structure
- Relationships between words
- Real-world facts
- Logic and reasoning
- Tone and style
- Common sense patterns
This is how an LLM becomes capable of writing paragraphs, answering questions, and generating meaningful content.
Step 4 – Adjusting Weights and Parameters
Every LLM contains millions—or more often billions—of parameters. These parameters act like tiny adjustable knobs inside the neural network. During training, the model tweaks these parameters in response to errors.
If the model predicts incorrectly → parameters adjust
If it predicts correctly → parameters strengthen
This continuous adjustment is powered by techniques such as:
- Backpropagation — sending error signals backward through the network
- Gradient descent — finding the direction that reduces error the most
Over time, the model becomes more accurate and better at predicting language, similar to how a person becomes more skilled with consistent practice.
Step 5 – Fine-Tuning for Better Behavior
After the initial “base training,” the model is powerful but not yet aligned with human expectations. This is why a second stage of training is applied to make the model more helpful, safe, and conversational.
Fine-tuning may involve:
- Instruction tuning:
Training the model to follow user instructions clearly and reliably. - Alignment training:
Teaching the model to avoid harmful, biased, or irrelevant responses. - Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF):
Humans rate different model responses, and the model learns which ones are best.
These steps help shape the model’s personality, clarity, safety, and usefulness—turning raw intelligence into a polished and helpful assistant.
The Transformer Architecture: The Core of LLMs
At the center of every modern Large Language Model is a groundbreaking innovation called the Transformer. Introduced in 2017, the Transformer completely reshaped the field of artificial intelligence by offering a faster, more powerful way for models to understand complex language. Instead of reading text word by word in order—like older systems did—the Transformer can look at an entire sentence or paragraph at once and understand how each word relates to every other word.
This ability makes Transformers incredibly good at capturing context. For example, take the sentences:
“John went to the store. He bought milk.”
A language model must understand that “He” refers to John, even though the words are separated. Transformers can recognize this connection instantly, and they do it through a powerful mechanism called self-attention.
What Is Self-Attention?
Self-attention is the secret ingredient that allows LLMs to focus on the right words at the right time. Instead of treating every word equally, the model learns to give more “attention” to the words that matter most for understanding meaning.
A simple example makes this clearer:
Sentence:
“The dog who chased the cat was brown.”
To understand the main idea, the model needs to connect:
- “dog” ↔ “was brown”
and not - “cat” ↔ “was brown.”
Self-attention helps the model recognize that the dog—not the cat—is the subject being described. It learns these relationships automatically during training, and once mastered, it can apply them across millions of different sentences.
The beauty of self-attention is that it works across long distances. Even if the related words are far apart, the model can still link them together, giving LLMs a level of linguistic understanding that older AI systems simply couldn’t achieve.
Layers, Heads, and Depth
Transformers are built from multiple repeating units, each designed to help the model understand deeper and more complex patterns in language.
They typically contain:
- Multiple layers — like stacked levels of understanding
- Multiple attention heads — allowing the model to focus on many relationships at once
Each layer in a Transformer learns something different:
- Early layers focus on grammar, word structure, and simple patterns.
- Middle layers learn context, writing style, and sentence flow.
- Final layers capture reasoning, relationships, and long-range dependencies across paragraphs or documents.
The more layers a model has, the deeper and more capable it becomes. This is why larger models—those with dozens or hundreds of layers—perform better at reasoning, creativity, and complex problem-solving.
How LLMs Generate Language
Once an LLM has completed its training, it’s ready to use everything it has learned to create new text. This is where the model shows its true power. Whether you ask it to write an email, explain a science concept, or summarize a long article, the model follows a predictable—but incredibly fast—process to produce meaningful language.
At its core, an LLM generates text by predicting one word at a time, using the patterns it learned during training. But because it does this thousands of times per second, the result feels natural, fluent, and human-like.
Step-by-Step Text Generation Process
Let’s break the process into simple steps to see how it works from your prompt to the final answer.
1. You give a prompt
Example:
“Explain solar energy in simple terms.”
2. The model turns the prompt into tokens
Text is converted into small units like words or parts of words so the model can understand it mathematically.
3. It predicts the next word (token)
The model uses all the patterns it learned during training to guess what should come next.
4. That word becomes part of the input
Each new predicted token is added back into the sentence.
5. The model predicts again—and again
This loop continues rapidly until the model produces a complete answer.
Because the model repeats this step thousands of times per second, it can generate paragraphs of clear, meaningful text almost instantly.
Temperature, Top-k, and Sampling
Not all text generation is the same. LLMs allow different settings to control how creative, safe, or bold the output should be. These settings shape the “personality” of the response.
Temperature — controls creativity level
- Low temperature (e.g., 0–0.3)
- Simple, predictable, factual
- Great for explanations, instructions, and technical writing
- High temperature (e.g., 0.7–1.2)
- More imaginative, surprising, and creative
- Useful for stories, ideas, brainstorming
Top-k and Top-p Sampling — filters out weak options
- Top-k limits the model to the top k best word choices
- Top-p lets the model choose from a dynamic set of top probabilities
These techniques help the model avoid strange or low-quality outputs, ensuring smoother, more useful responses.
Because of these settings, LLMs can easily switch between:
- Structured, professional text (formal writing, reports, explanations)
- Creative, expressive text (poetry, stories, brainstorming ideas)
In short, the way an LLM generates language is a mix of learned knowledge, mathematical prediction, and fine-tuning with creativity controls—working together to produce natural and intelligent responses.
Why LLMs Seem “Smart”: Emergent Abilities
One of the most fascinating things about Large Language Models is that as they get bigger, they begin to show abilities that were never directly programmed into them. These skills appear naturally as the model is trained on massive amounts of text, almost like the model is discovering new capabilities on its own. This phenomenon is known as emergent abilities.
Emergent abilities are skills the model was not specifically taught, yet it learns anyway by recognizing patterns across billions of sentences. As the number of parameters increases and the training data expands, the model starts connecting concepts in deeper and more human-like ways.
Some of the most impressive emergent abilities include:
- Summarization – Understanding long content and shortening it meaningfully
- Translation – Converting text between languages with surprising accuracy
- Logical reasoning – Solving problems by following patterns of logic
- Math solving – Handling arithmetic and even some algebraic steps
- Programming – Writing and debugging code in multiple languages
- Step-by-step reasoning – Breaking down solutions into clear processes
- Context understanding – Recognizing subtle relationships within text
What makes this even more remarkable is that the model was not explicitly trained for many of these tasks. Instead, it learned them by absorbing patterns from huge datasets—just as humans learn by observing the world around them.
This is why LLMs can appear “smart”: their scale allows them to pick up abilities that go far beyond simple prediction, giving them a level of versatility that feels increasingly close to real intelligence.
Limitations of LLMs (Honest Breakdown)
Large Language Models are impressive, but like any technology, they come with real limitations. Understanding these limitations is important because it helps users know when to trust an LLM—and when to double-check its answers. Below is a clear, honest look at the areas where LLMs still fall short.
1. Lack of True Understanding
Even though LLMs appear intelligent, they do not actually understand the world the way humans do.
LLMs operate purely on patterns, not meaning or awareness.
- They don’t form opinions
- They don’t have experiences
- They don’t “know” things—they predict based on data
An LLM may sound confident and thoughtful, but behind the scenes, it is simply using statistical relationships between words.
2. Hallucinations (Confident Wrong Answers)
One of the biggest issues with LLMs is that they sometimes produce answers that sound accurate—even when they are completely wrong. These are called hallucinations.
Examples include:
- Citing nonexistent studies
- Giving made-up facts
- Creating incorrect code snippets
- Filling gaps with fictional information
Because LLMs prioritize fluency and confidence, these errors can be misleading unless the user verifies the information.
3. Outdated Knowledge
LLMs do not automatically stay updated.
Unless they:
- connect to real-time tools
- access the internet
- or receive regular training updates
…their knowledge remains limited to the data they were originally trained on.
This means an LLM might miss:
- recent news
- new research
- updated regulations
- fresh trends
- product releases
Without external tools, the model can only operate based on past information.
4. Bias in Training Data
Because LLMs learn from human-generated text, they are exposed to the same biases that exist in society. If the training data includes:
- cultural bias
- gender bias
- political bias
- stereotypes
…the model may unintentionally repeat or amplify those biases.
This is why developers use alignment and safety training to reduce harmful patterns—but bias can never be fully eliminated.
5. High Computation Cost
Training large models requires enormous computing power. Cutting-edge LLMs often need:
- thousands of GPUs
- massive data centers
- weeks or months of training time
- millions of dollars in electricity and hardware costs
Because of this, only a few companies in the world currently have the resources to train very large models from scratch.
What Makes Modern LLMs So Powerful?
Modern Large Language Models may feel magical, but their strength comes from a combination of advanced training methods, massive datasets, and breakthrough architectures. These elements work together to give LLMs the ability to understand instructions, reason through problems, and generate human-like responses with surprising accuracy.
Below are the core factors that make today’s LLMs so powerful and versatile.
A. Massive Data
One of the biggest advantages of modern LLMs is the sheer volume of text they are trained on.
They absorb information from:
- Books
- Academic papers
- Online articles
- Websites
- Code bases
- Social media content
- Multilingual datasets
The more text a model reads, the more patterns it learns. It begins to understand grammar, logical relationships, tone, writing styles, and real-world facts. This deep exposure allows LLMs to generate responses that feel natural and context-aware.
Simply put:
More data = better language understanding.
B. Billion-Parameter Scale
Another massive leap in AI power comes from model size.
Modern LLMs have:
- Billions
- And sometimes trillions of parameters
Parameters are the tiny internal values that help the model decide which words, ideas, or responses are most likely.
With more parameters, the model can:
- Capture deeper patterns
- Understand complex relationships
- Follow multi-step logic
- Provide more accurate answers
- Handle long, detailed prompts
This is why larger models tend to be better at tasks like reasoning, coding, summarizing, and translating.
More parameters = deeper reasoning and intelligence.
C. Reinforcement Learning and Alignment
Raw intelligence isn’t enough.
A model must also learn how to be useful, safe, and aligned with human expectations.
This is where training methods like:
- Instruction tuning
- Human feedback evaluation
- RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback)
come into play.
During this phase, humans review responses, rank them, and guide the model toward:
- clearer explanations
- safer outputs
- more helpful behavior
- better reasoning
- reduced bias
This alignment step transforms the model from a “text predictor” into a helpful conversational assistant that understands nuance and intent.
D. Multimodality
The newest generation of LLMs no longer rely on text alone.
They can understand and process multiple forms of information, including:
- Text
- Images
- Audio
- Code
- Video
- Documents (PDFs, spreadsheets, etc.)
This multimodal capability makes them dramatically more versatile.
For example, modern LLMs can:
- Analyze images and describe what’s happening
- Read documents and summarize the key points
- Interpret charts and extract insights
- Understand video frames or audio transcripts
- Combine text and visuals to answer complex questions
This evolution moves LLMs closer to general intelligence—tools that can interact with the world in multiple ways, not just through written language.
Real-World Use Cases of LLMs
Large Language Models are no longer experimental—they are transforming real industries every day. Their ability to generate text, analyze information, and understand context makes them valuable tools in business, education, healthcare, finance, and creative work. Below are some of the most impactful ways LLMs are being used across different fields.
i) Business
In the business world, LLMs act as intelligent digital assistants that streamline operations and reduce manual work. They help teams save time, improve communication, and deliver better customer experiences.
LLMs are widely used for:
- Customer support: powering chatbots that answer questions instantly
- Email automation: drafting replies, sorting messages, and creating templates
- Report generation: turning raw data into readable business summaries
- Sales & marketing content: crafting product descriptions, ads, and newsletters
- Productivity assistants: helping managers with planning, scheduling, and research
As companies scale, these tools dramatically improve efficiency.
ii) Education
In education, LLMs act as personal learning companions. They support students and teachers by simplifying complex topics and offering guidance anytime.
Common educational uses include:
- Tutoring: explaining subjects step-by-step in simple language
- Notes summarization: condensing long chapters or lectures
- Assignment help: offering feedback or structuring essays
- Language learning: providing translations, examples, and practice conversations
This makes learning more personalized and accessible to everyone.
iii) Software Development
Developers benefit enormously from LLMs because these models understand and generate code almost like a programming partner.
Key applications include:
- Code generation: writing functions, modules, or entire project templates
- Debugging: identifying errors and suggesting fixes
- Documentation: creating explanations, comments, or API guides
Tools such as GitHub Copilot, Cursor, and many IDE plugins rely on LLMs to speed up development and reduce repetitive tasks.
iv) Healthcare
In healthcare, LLMs support medical professionals by helping them manage information-heavy workflows where accuracy and clarity are essential.
Popular use cases:
- Medical summaries: converting long records into easy-to-read reports
- Patient report analysis: identifying important trends or symptoms
- Research synthesis: summarizing clinical studies and medical literature
While LLMs don’t replace doctors, they help reduce administrative load and improve decision-making.
v) Finance
Financial institutions use LLMs to enhance risk management, security, and reporting. These models can analyze patterns that humans might miss.
Common applications:
- Risk analysis: evaluating financial documents and forecasting risks
- Fraud detection: identifying suspicious patterns in transactions
- Analytical automation: generating financial summaries, charts, and insights
This leads to faster, smarter, and more reliable financial operations.
vi) Creativity and Media
LLMs have quickly become creative partners for content creators, marketers, filmmakers, and writers. Their ability to generate ideas makes them invaluable in the creative process.
They help with:
- Scriptwriting: drafting scenes, dialogues, or full video scripts
- Video concept generation: brainstorming ideas for reels, shorts, and ads
- Storytelling: creating narratives, characters, and plotlines
- Graphic outlines: providing design prompts, layout ideas, and visual concepts
Rather than replacing creativity, LLMs amplify it by giving creators a constant source of inspiration.
The Future of Large Language Models
Large Language Models are advancing at an incredible pace. What began as simple text-prediction engines is now transforming into highly capable, multimodal, and intelligent systems. The next generation of LLMs will be even more powerful, more personal, and more deeply integrated into our daily lives. Here’s what the future of LLMs is shaping up to look like.
1. Smaller & Faster Models
In the near future, we will see a shift toward compact, efficient LLMs that run locally on everyday devices.
These “edge models” will operate on:
- phones
- laptops
- tablets
- even smart home devices
This means users can enjoy instant responses, improved privacy, and offline AI capabilities—without relying on cloud servers. Faster, lighter models will make AI accessible to everyone, everywhere.
2. Real-Time Reasoning Agents
Today’s LLMs mostly answer questions. Tomorrow’s LLMs will take action.
Future AI agents will:
- automate entire workflows
- navigate websites and tools independently
- solve multi-step tasks
- make decisions based on goals
- act as digital co-workers rather than just assistants
This evolution will move LLMs from “conversation partners” to action-driven AI agents that handle real operations in real time.
3. True Multimodal Intelligence
The next wave of LLMs won’t rely only on text—they will understand and process information the same way humans do.
Upcoming LLMs will be able to:
- see images
- hear audio
- read PDFs and spreadsheets
- watch videos
- interpret charts
- analyze environments
This will create AI systems capable of solving complex problems across multiple mediums at once. Imagine an AI that can read your document, look at your diagram, analyze your screenshot, and explain all of it together.
4. Personalized AI
A major development ahead is deep personalization.
Each user will have their own AI “digital twin”—a model that learns:
- your preferences
- your writing style
- your work habits
- your goals
- your routines
This personalized AI will assist with daily tasks, manage information, and anticipate your needs. It will feel less like a generic chatbot and more like a long-term intelligent partner.
5. More Transparent AI
As AI becomes more widespread, users will want to understand how decisions are made. The future of LLMs will include:
- explainable reasoning
- clear decision pathways
- improved safety mechanisms
- transparent model behavior
This shift toward explainability will help people trust AI outputs and verify the accuracy of results, especially in sensitive fields like healthcare, law, and finance.
Final Thoughts: Why Understanding LLMs Matters Today
LLMs are rapidly becoming the backbone of modern AI, powering tools that shape how we work, learn, communicate, and create. Understanding how these systems learn, generate text, and make decisions is essential for using them confidently and responsibly. The more familiar users become with LLMs, the better they can leverage their potential—and avoid their pitfalls.
As AI continues evolving toward multimodal intelligence, personalized assistants, and autonomous agents, we are entering an era where AI becomes a natural extension of human capability. Knowing the basics today prepares individuals and businesses for a future where intelligent systems play an even greater role in daily life.
