Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broad concept of making machines act smart, Machine Learning (ML) is a method within AI that allows systems to learn from data, and Deep Learning (DL) is a specialized branch of ML that uses neural networks to process complex patterns. In simple terms, AI is the big goal, ML is the method, and DL is the most advanced form of that method.
Though people often use these terms interchangeably, they are not the same. Understanding the difference is crucial for students, professionals, business owners, and anyone curious about today’s smart technology.
Let’s break it down clearly and simply.
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence is the science of building machines that can simulate human intelligence. AI systems can think, analyze, understand language, recognize images, and make decisions—just like humans, but powered by algorithms and computing power.
What AI Can Do
AI enables machines to:
- Understand human speech
- Recognize faces and objects
- Make predictions and recommendations
- Play games and beat humans
- Drive cars
- Write content
- Detect fraud
- Diagnose diseases
AI doesn’t always learn by itself. Some AI systems are built using hard-coded rules, while others rely on data-driven learning (which is where ML and DL come in).
Types of AI
- Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Designed for one specific task (voice assistants, recommendation engines, chatbots). - General AI (Strong AI – Still Theoretical)
Can perform any intellectual task like a human. This doesn’t truly exist yet. - Super AI (Future Concept)
Smarter than humans in all areas. Still science fiction.
Today, almost everything we call “AI” is actually Narrow AI powered by Machine Learning.
What Is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that allows machines to learn from data instead of being manually programmed for every task.
Instead of writing rules like:
“If customer buys X, show Y,”
Machine Learning finds those patterns automatically by analyzing data.
How Machine Learning Works (Simple Explanation)
- You feed the system data
- The system analyzes patterns
- It learns from examples
- It makes predictions on new data
For example:
- Spam email detection
- Product recommendations
- Fraud alerts
- Price predictions
All of these use Machine Learning models trained on past data.
What Is Deep Learning (DL)?
Deep Learning is a specialized branch of Machine Learning that uses artificial neural networks inspired by the human brain.
It is called “deep” because it uses multiple layers of neural networks to process complex information.
Deep Learning is what powers:
- Face recognition
- Self-driving cars
- Voice assistants
- Medical image detection
- Language translation
- AI-generated images and videos
Why Deep Learning Is So Powerful
Traditional ML needs humans to manually define features.
Deep Learning learns features by itself.
For example:
- ML needs humans to define “eyes,” “nose,” “edges”
- DL automatically learns what a face looks like from raw pixels
That’s what makes it revolutionary.
AI vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning (Simple Comparison)
| Feature | AI | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Broad concept of smart machines | AI that learns from data | ML that uses neural networks |
| Human Intervention | High | Medium | Low |
| Data Need | Low to medium | Medium | Very high |
| Hardware Requirement | Low | Medium | Very high (GPUs) |
| Example | Chatbots, Expert Systems | Recommendation engines | Facial recognition |
| Learning Ability | Optional | Yes | Yes (advanced) |
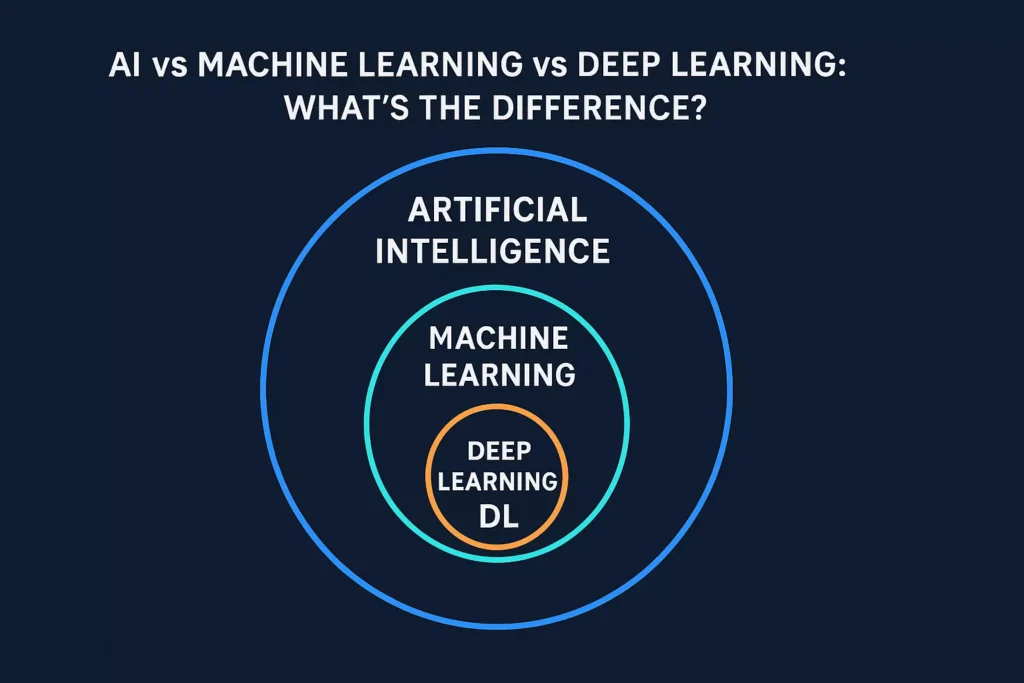
Relationship Between AI, ML, and DL
Think of it like this:
- AI is the universe
- Machine Learning is a planet inside AI
- Deep Learning is a country inside that planet
Or another simple comparison:
- AI = Goal (make machines smart)
- ML = Method (machines learn from data)
- DL = Tool (neural networks that mimic the brain)
All Deep Learning is Machine Learning.
All Machine Learning is Artificial Intelligence.
But not all AI uses ML, and not all ML uses DL.
How AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning Are Used in Real Life
1. Smartphones: Making Devices Smarter Every Day
Modern smartphones are a perfect example of how AI, ML, and DL work together to create intelligent user experiences.
- Artificial Intelligence powers voice assistants that understand commands, answer questions, manage schedules, and control smart devices. AI also helps manage battery usage and optimize system performance.
- Machine Learning studies your typing habits, app usage, and browsing behavior to predict your next word, suggest apps you are likely to open, and personalize notifications.
- Deep Learning enables advanced face recognition, fingerprint unlocking, real-time photo enhancement, object detection in images, and portrait-mode photography.
Together, these technologies turn smartphones into highly personalized digital companions.
2. Healthcare: Saving Lives with Intelligent Systems
The healthcare industry has seen one of the most powerful transformations through AI-driven technologies.
- Artificial Intelligence supports doctors with automated diagnosis systems, virtual health assistants, patient management tools, and smart hospital operations.
- Machine Learning analyzes patient history, lab reports, genetic data, and lifestyle patterns to predict disease risks such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer at early stages.
- Deep Learning is capable of scanning X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and ultrasound images with extreme precision, often detecting tumors and abnormalities that the human eye might miss.
In many cases, these systems improve early detection, reduce human error, and enhance treatment planning.
3. Online Shopping: Creating Personalized Buying Experiences
E-commerce platforms rely heavily on AI to increase customer satisfaction and boost sales.
- Artificial Intelligence powers customer support chatbots that answer queries 24/7, handle returns, track orders, and solve basic problems instantly.
- Machine Learning studies your browsing history, past purchases, and product searches to recommend items you are most likely to buy.
- Deep Learning goes a step further by dynamically adjusting product prices, optimizing advertisements in real time, and creating hyper-personalized shopping experiences based on detailed user behavior.
This is why two people often see completely different product suggestions on the same shopping website.
4. Banking and Finance: Enhancing Security and Accuracy
Financial institutions depend on AI-driven systems to manage massive volumes of sensitive data securely.
- Artificial Intelligence monitors customer transactions in real time to instantly detect suspicious activities and prevent fraud.
- Machine Learning predicts stock price movements, detects irregular trading patterns, and calculates credit scores based on financial behavior.
- Deep Learning analyzes complex financial data across global markets, identifying hidden trends and risks within massive datasets that traditional systems cannot process efficiently.
These technologies help banks improve security, increase profits, and offer personalized financial services.
5. Self-Driving Cars: Powering the Future of Transportation
Autonomous vehicles represent one of the most advanced real-world applications of AI, ML, and DL working together.
- Artificial Intelligence acts as the decision-making brain that controls overall driving behavior, route planning, braking, steering, and speed adjustments.
- Machine Learning learns traffic patterns, driver behaviors, and road conditions to predict how vehicles and pedestrians might move in different situations.
- Deep Learning uses cameras, radar, and sensors to instantly recognize pedestrians, traffic lights, stop signs, road lanes, cyclists, animals, and obstacles with high accuracy.
Together, these technologies allow vehicles to see, think, learn, and react—bringing truly autonomous transportation closer to reality.
Difference in Learning Capabilities
AI Without Machine Learning: Rule-Based Intelligence
Some AI systems operate without any learning ability at all. These are known as rule-based AI systems, where every action is controlled by clearly defined instructions.
In this approach:
- The system follows fixed “if–then” rules, such as: If this happens, then perform that action.
- There is no ability to learn from experience or improve automatically.
- The system functions reliably only in controlled and predictable environments.
- Any change in behavior requires manual reprogramming by developers.
Example: Early chess programs that played based on pre-defined strategies. They could follow strong rules but could not evolve beyond what was programmed into them.
Machine Learning Learning Style: Learning from Structured Data
Machine Learning systems learn from data rather than explicit rules. These systems improve their performance over time by analyzing examples and identifying patterns.
In this learning method:
- The system is trained on structured, labeled data.
- It learns by connecting input data with correct outcomes.
- Performance improves gradually as more data becomes available.
- Humans must still perform feature engineering, meaning they define what data patterns the model should focus on.
Example: Predicting house prices using factors like location, size, number of rooms, and past sales data.
Deep Learning Learning Style: Learning Directly from Raw Data
Deep Learning represents the most advanced form of machine learning. It uses multi-layered neural networks to process information in a way similar to the human brain.
In this learning approach:
- The system learns directly from raw, unstructured data, such as images, audio, and video.
- It does not require manual feature selection, as it automatically discovers important patterns.
- It can handle extremely complex tasks like speech recognition, image detection, and language translation.
- It requires massive datasets, high computing power, and specialized hardware such as GPUs.
Example: Face recognition technology on smartphones that can accurately identify individuals from camera images in real time.
Data Requirements: ML vs DL
One of the biggest differences between Machine Learning and Deep Learning lies in how much data they need to perform well—and the gap is massive.
Machine Learning models are highly effective even with:
- Thousands of data points, not millions
- Clean and well-structured datasets, such as spreadsheets and databases
- Clearly defined features selected by humans
Because of this, ML is widely used in business forecasting, customer analysis, and price prediction where data is organized and limited.
In contrast, Deep Learning systems are data-hungry and power-intensive. They typically require:
- Millions (or even billions) of data points to achieve high accuracy
- Unstructured data such as images, videos, audio, and natural language
- Advanced computing power, including GPUs and TPUs, to train deep neural networks efficiently
This massive demand for data and processing power is the main reason Deep Learning only became truly practical in the last decade, when high-performance hardware became more affordable and accessible. Without modern GPUs and cloud computing, today’s AI breakthroughs in vision, speech, and automation would not be possible.
Accuracy Comparison
Accuracy is one of the most important factors when evaluating intelligent systems, and this is where the differences between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning become very clear.
- Rule-based AI systems offer limited accuracy because they rely entirely on fixed instructions. They perform well only in predictable environments and struggle when unexpected situations arise.
- Machine Learning models achieve strong and reliable accuracy when they are trained on high-quality, well-prepared data. The better and more relevant the data, the more accurate their predictions become.
- Deep Learning systems deliver exceptionally high accuracy, especially when trained on massive datasets. Because they can automatically learn complex patterns from raw data, they consistently outperform traditional models in advanced tasks.
This is exactly why Deep Learning dominates today’s most demanding AI applications, including:
- Medical imaging, where detecting tiny abnormalities can save lives
- Autonomous driving, where vehicles must interpret the world in real time
- Voice recognition, enabling natural conversations with devices
- AI-generated content, such as realistic images, videos, and human-like text
Cost Comparison
| Technology | Cost Level |
|---|---|
| AI (Rule-Based) | Low |
| Machine Learning | Medium |
| Deep Learning | High |
Deep Learning is expensive because:
- Requires GPUs
- Needs massive storage
- Longer training time
- Higher energy usage
Skill Requirements for Each
Skills Required for an AI Developer
An AI developer focuses on building intelligent systems using logic, rules, and core programming techniques. Key skills include:
- Strong logical thinking to design decision-based systems
- Understanding of algorithms to solve problems efficiently
- Programming skills in languages like Python or Java
- Basic data handling skills for managing and processing information
AI developers often work on automation systems, chatbots, expert systems, and rule-based applications.
Skills Required for a Machine Learning Engineer
Machine Learning engineers specialize in creating systems that learn from data. Their skill set requires deeper mathematical and analytical knowledge:
- Strong foundation in statistics and probability
- Data science expertise for cleaning, analyzing, and preparing datasets
- Programming skills in Python and R
- Hands-on experience with model training and evaluation
They build recommendation systems, prediction models, fraud detection tools, and demand forecasting systems.
Skills Required for a Deep Learning Engineer
Deep Learning engineers work on the most advanced AI systems that mimic how the human brain processes information. Their role demands cutting-edge skills and high-performance computing knowledge:
- Expertise in neural networks and deep architectures
- Proficiency in frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch
- Experience with GPU-based computing for fast model training
- Ability to handle massive datasets and big data pipelines
They build facial recognition systems, voice assistants, medical imaging engines, and autonomous vehicle intelligence.
Myths About AI, ML, and DL
Myth 1: AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning Are the Same Thing
This is one of the most widespread misconceptions. While closely related, they are not identical.
The truth:
Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning, and Machine Learning is a subset of Artificial Intelligence. AI is the broad concept, ML is one approach to achieving AI, and DL is the most advanced learning technique within ML.
Myth 2: AI Is Replacing All Human Jobs
Many people fear that AI will eliminate most jobs, but the reality is far more balanced.
The truth:
AI is reshaping and enhancing jobs, not wiping them out entirely. While some repetitive tasks are becoming automated, new roles in AI development, data science, cybersecurity, and automation are emerging faster than ever. Human skills like creativity, strategy, empathy, and leadership remain irreplaceable.
Myth 3: AI Thinks and Feels Like Humans
Movies often portray AI as conscious and emotional, which leads to unrealistic expectations.
The truth:
Today’s AI systems do not think, feel, or possess self-awareness. They only imitate intelligence by analyzing data and following programmed patterns. AI has no emotions, intentions, or consciousness—only computation.
Future of AI, ML, and DL
The Future of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is moving beyond basic automation toward truly intelligent assistance. In the coming years, we can expect:
- Smarter automation that can handle complex business processes with minimal human input
- Personal AI agents that manage daily tasks, schedules, finances, and communication
- Autonomous industries, including factories, logistics, and customer service operations
- Stronger human–AI collaboration, where machines enhance human creativity, productivity, and decision-making
AI will shift from being a tool we “use” to a partner that actively supports our goals.
The Future of Machine Learning
Machine Learning will become more powerful, faster, and more self-reliable as data access and computing improve. Key developments will include:
- Higher predictive accuracy, allowing businesses to forecast trends with greater confidence
- Real-time insights, enabling instant decision-making across industries
- AI-powered decision systems that help humans choose the best actions using continuous data analysis
ML will no longer just analyze the past—it will increasingly shape the future in real time.
The Future of Deep Learning
Deep Learning will continue to drive the most dramatic breakthroughs in AI innovation. In the near future, we are likely to see:
- Fully autonomous vehicles operating safely on public roads
- Major medical breakthroughs, including early disease detection and AI-driven drug discovery
- Human-like voice and vision systems, making AI interaction feel more natural and intuitive
As deep neural networks become more efficient and less energy-hungry, their real-world use will expand rapidly.
Business Impact of AI vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning are no longer experimental technologies—they are now powerful business tools driving growth, efficiency, and innovation across industries.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) helps businesses reduce customer service costs by automating support through chatbots, virtual assistants, and smart ticketing systems.
- Machine Learning (ML) significantly improves sales accuracy by predicting customer behavior, demand trends, and purchasing decisions.
- Deep Learning (DL) powers large-scale innovation, enabling breakthroughs in areas like medical imaging, autonomous systems, smart manufacturing, and content generation.
Companies that actively use these technologies gain major competitive advantages, including:
- Faster decision-making through real-time data analysis
- Lower operational costs through automation
- Higher customer satisfaction through personalized experiences
- Stronger security through intelligent fraud and threat detection
This is exactly why nearly every major industry—from healthcare and finance to retail and transportation—is investing heavily in AI, ML, and DL to stay future-ready.
Which One Should You Learn First?
If you’re just starting your journey in this field, the right learning path makes all the difference.
As a beginner, you should follow this order:
- Start with AI basics to understand how intelligent systems work
- Move to Machine Learning fundamentals to learn how systems improve using data
- Then advance to Deep Learning, where you work with neural networks and complex models
Jumping directly into Deep Learning without understanding Machine Learning often leads to confusion, frustration, and weak foundations. A step-by-step approach ensures stronger skills, better projects, and long-term career success.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the difference between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning is no longer just for engineers—it’s essential knowledge for anyone living in today’s digital world. From your smartphone camera to your bank’s fraud detection system, these technologies silently shape your life every second.
- AI gives machines intelligence.
- Machine Learning teaches them how to learn.
- Deep Learning gives them vision, hearing, and deep understanding.
Together, they form the backbone of the future.