AI in manufacturing means using artificial intelligence to automate tasks, improve production quality, reduce downtime, and make factories smarter, faster, and more efficient. Today’s modern factories rely heavily on AI systems to predict equipment failures, optimize workflows, inspect products, and support decision-making in real time.
AI is no longer a future trend—it’s the new backbone of modern manufacturing, transforming how factories operate across every industry.
Why AI Is Transforming Manufacturing
Manufacturing is one of the world’s most complex and fast-moving industries. It involves thousands of processes, machines, and decisions happening every second. Traditional methods simply can’t keep up with the demands for speed, accuracy, and cost-efficiency.
This is where AI creates a massive shift.
AI-powered automation helps factories eliminate guesswork, streamline tasks, maintain consistent quality, and respond quickly to production challenges. Whether it’s predictive maintenance, defect detection, robotics, or supply chain optimization—AI makes manufacturing operations smarter at every level.
What Does AI Mean in Manufacturing?
AI in manufacturing refers to the integration of advanced artificial intelligence technologies into factory operations to improve how products are designed, produced, and delivered. It includes systems and tools such as machine learning, computer vision, predictive analytics, advanced robotics, natural language processing, and digital twins—all working together to create smarter, more efficient production environments.
These AI technologies enable factories to:
- Automate repetitive and manual tasks, allowing workers to focus on higher-value responsibilities.
- Predict and prevent machine failures, reducing unexpected downtime and maintenance costs.
- Increase overall production output by optimizing workflows and ensuring machines operate at peak efficiency.
- Improve product quality through real-time inspections and defect detection powered by computer vision.
- Enhance worker safety by assisting in hazardous jobs and monitoring unsafe conditions.
- Minimize operational costs across labor, materials, energy, and maintenance.
- Support better decision-making by using real-time data, insights, and AI-driven recommendations.
AI doesn’t replace human workers—it empowers them. By turning raw data into actionable intelligence, AI gives manufacturers deeper visibility into every part of the production process, helping them operate with greater accuracy, consistency, and confidence.
Data & Statistics: The Real Impact of AI on Manufacturing
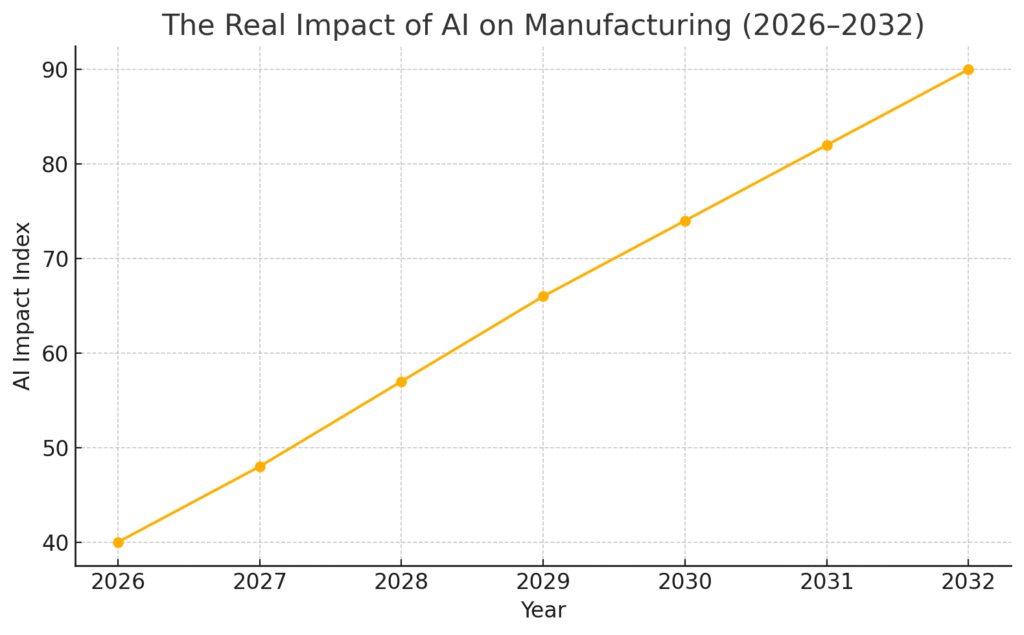
- 76% of manufacturers use AI in at least one operation.
- AI boosts factory productivity by 20–40%.
- Predictive maintenance cuts downtime by 30% and reduces maintenance costs by 15–25%.
- AI quality inspection achieves up to 98% accuracy and reduces defects by 30–50%.
- AI improves supply chain forecasting by 50% and cuts delivery delays by 35%.
- 64% of companies say AI boosts worker productivity rather than replacing jobs.
- AI reduces energy usage by 10–20% and lowers carbon emissions by 15%.
- AI-led manufacturers report 25% higher profit margins.
- The AI in manufacturing market will reach $68.4B by 2026.
How AI Enhances Manufacturing Efficiency
In modern manufacturing, operational efficiency determines productivity, profitability, and long-term competitiveness. Even small improvements in speed, accuracy, or machine performance can create significant financial impact. Artificial intelligence elevates efficiency by bringing intelligence, automation, and precision to every part of the production cycle.
Below is a structured overview of how AI strengthens manufacturing efficiency:
1. Automated Production Processes
AI-enabled automation allows machines, robots, and systems to operate continuously with minimal intervention. This ensures:
- Consistent production quality
- Faster cycle times
- Reduced human error
- Increased throughput across shifts
Automation drives predictable, stable, and scalable production performance.
2. Accelerated, Data-Driven Decision-Making
AI analyzes real-time operational data from sensors, machines, and manufacturing lines, enabling:
- Immediate detection of anomalies
- Rapid response to process fluctuations
- Smarter scheduling and resource allocation
This level of instant insight helps leaders prevent disruptions before they escalate.
3. Enhanced Quality Control and Defect Reduction
AI-powered computer vision systems perform microscopic inspections at speeds far beyond human capability. They help detect:
- Surface imperfections
- Dimensional deviations
- Material inconsistencies
- Assembly errors
The result is fewer defects, reduced rework, and better overall product reliability.
4. Workflow and Process Optimization
Using advanced analytics, AI evaluates production patterns to identify inefficiencies. It can:
- Uncover hidden bottlenecks
- Predict slowdowns
- Recommend process improvements
- Balance workloads across machines
This ensures smooth, synchronized production flow across all departments.
5. Maximized Machine Utilization
AI improves machine performance through predictive maintenance and continuous monitoring. It enhances:
- Equipment uptime
- Asset life cycles
- Maintenance planning
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
By minimizing unplanned downtime, manufacturers achieve more output with fewer disruptions.
Key Applications of AI in Modern Factories
i) Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance leverages AI to anticipate equipment failures well before they occur by continuously analyzing sensor data. Sensors capture metrics such as temperature, vibration, acoustic signatures, and pressure; machine learning models then identify subtle patterns and anomalies that precede breakdowns.
Benefits:
- Reduced downtime; unplanned stoppages are minimized.
- Extended equipment lifetime through timely interventions.
- Lower repair costs by addressing issues early.
- Stable production with fewer interruptions. Across manufacturing sectors, predictive maintenance is one of the fastest‑adopted AI use cases because it delivers measurable uptime and cost improvements.
ii) Computer Vision for Quality Inspection
AI-driven computer vision systems automate visual inspection at scale, inspecting thousands of units per hour with consistency and precision beyond human capability. These systems use high‑resolution imaging and trained models to detect a wide range of defects, from visible surface blemishes to microscopic irregularities.
What AI can detect:
- Surface defects such as scratches, dents, and contamination.
- Shape irregularities and dimensional deviations.
- Color mismatches and printing errors.
- Structural faults and assembly mistakes.
- Microscopic flaws that escape manual inspection. By integrating computer vision, manufacturers improve product quality, reduce scrap and rework, and strengthen customer trust.
iii) Intelligent Robotics
Intelligent robotics combines advanced AI with robotic hardware to create flexible, adaptive automation that goes beyond repetitive tasks. These robots can learn new operations, adjust to changing production requirements, and safely collaborate with human colleagues on shared tasks.
Capabilities:
- Human-robot collaboration for mixed workflows.
- On-the-fly learning to accommodate new parts or processes.
- Environmental adaptability to handle variability on the line.
- High-precision handling for delicate or complex assembly.
- Safe operation around people through perception and control systems. Industries such as automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods rely on intelligent robots to increase throughput while maintaining flexibility.
iv) Real-Time Production Monitoring
Real-time production monitoring uses AI to continuously observe manufacturing processes and make immediate adjustments that preserve quality and throughput. These systems fuse data from machines, sensors, and control systems to detect deviations and optimize parameters in the moment.
Typical adjustments:
- Machine speed tuning to match process conditions.
- Line balancing to prevent bottlenecks.
- Energy optimization to reduce consumption during low-demand periods.
- Delay identification to trigger corrective actions. The result is greater process consistency, improved equipment utilization, and faster response to anomalies.
v) Supply Chain Optimization
AI transforms supply chain management by providing predictive insights and prescriptive actions across planning, procurement, and logistics. Models forecast demand more accurately, optimize inventory levels, and recommend efficient routing and supplier choices.
Key improvements:
- Demand forecasting that reduces overstock and stockouts.
- Inventory management tuned to real consumption patterns.
- Stockout prevention through proactive replenishment.
- Route optimization for faster, lower‑cost deliveries.
- Supplier evaluation using performance and risk analytics. End‑to‑end visibility enabled by AI helps manufacturers respond faster to market shifts and maintain resilient operations.
vi) Digital Twins
A digital twin is a dynamic virtual replica of a factory, machine, or process that mirrors real‑world behavior using live data and simulation. AI powers these models to run scenarios, predict outcomes, and validate changes before they are implemented on the shop floor.
Primary uses:
- Production planning to test schedules and capacity changes.
- System troubleshooting to isolate root causes without disrupting operations.
- Performance prediction under varying loads and conditions.
- Layout optimization to evaluate material flow and ergonomics. Digital twins reduce implementation risk, accelerate decision cycles, and improve operational precision.
vii) AI for Worker Safety
AI enhances workplace safety by combining sensing, analytics, and automation to prevent accidents and protect worker health. Systems monitor behavior, environmental conditions, and physiological signals to identify hazards and trigger interventions.
Safety applications:
- Computer vision to detect unsafe actions or missing protective equipment.
- Wearable and ambient sensors to monitor worker health and exposure.
- Robotic handling of hazardous tasks to remove humans from risk.
- Predictive analytics to identify accident‑prone zones and times. Prioritizing AI‑driven safety measures is especially critical in heavy manufacturing, where the consequences of incidents are severe.
Benefits of AI in Manufacturing
Artificial intelligence brings a wide range of advantages to modern manufacturing, helping factories operate with greater efficiency, accuracy, and agility. From boosting productivity to improving the overall worker experience, AI is transforming how manufacturers plan, produce, and deliver goods. Below are the most impactful benefits AI provides.
A. Higher Productivity
AI-powered machines and automated systems operate with high speed, precision, and consistency. They can run continuously with minimal downtime, allowing production lines to achieve significantly higher output. By reducing manual intervention and eliminating human error, AI ensures smoother operations and maximizes overall productivity.
B. Lower Operational Costs
AI helps manufacturers cut costs across labor, materials, and maintenance. Automation handles repetitive tasks, reducing the need for manual labor. Predictive analytics prevent expensive breakdowns, and optimized processes minimize material waste. Together, these improvements lead to substantial savings and a more efficient cost structure.
C. Improved Product Quality
With AI-driven inspection tools and real-time monitoring, manufacturers can detect defects early and maintain strict quality standards. AI ensures that each product meets precise specifications, reducing rework and scrap rates. This results in more reliable products and strengthened brand reputation.
D. Faster Time–to-Market
AI accelerates every stage of production—from design to assembly. Technologies like digital twins, automated workflows, and predictive analytics streamline development processes and reduce delays. As a result, manufacturers can bring new products to market faster, staying ahead of competition and meeting customer demands quickly.
E. Enhanced Worker Experience
AI enhances the workplace by supporting employees rather than replacing them. It handles the repetitive and physically demanding tasks, allows workers to focus on more strategic responsibilities, and provides real-time insights to aid decision-making. This leads to a safer, more engaging, and more productive work environment.
F. Scalability
AI makes it much easier for factories to scale production without requiring large increases in manpower or physical resources. Automated processes, real-time optimization, and intelligent planning allow manufacturers to increase capacity smoothly while maintaining high efficiency and consistent quality.
AI-Powered Smart Factories
Modern smart factories are highly connected, data-driven environments where artificial intelligence orchestrates operations across machines, people, and processes. These facilities combine continuous sensing, advanced analytics, and automated control to transform raw data into immediate, actionable decisions. The result is a manufacturing ecosystem that adapts in real time, reduces waste, and consistently delivers higher quality at lower cost.
Core Capabilities of a Smart Factory
Smart factories deploy AI systems to perform a set of interlocking functions that keep production agile and resilient:
- Real-time workflow monitoring AI ingests streams of sensor and system data to provide continuous visibility into every stage of production. This enables instant detection of anomalies, bottlenecks, and deviations from target performance.
- Machine health prediction Predictive models analyze vibration, temperature, acoustic, and operational metrics to forecast equipment degradation and impending failures. This allows maintenance to be scheduled proactively, minimizing unplanned downtime.
- Automated quality inspection Computer vision and pattern-recognition algorithms inspect parts and assemblies at high speed and precision, identifying defects that are difficult or impossible for the human eye to catch.
- Coordination of robots and human workers AI plans and synchronizes tasks across collaborative robots and human operators, assigning work dynamically to maximize throughput while preserving safety and ergonomics.
- Energy optimization Intelligent control systems balance production needs with energy consumption, adjusting machine cycles, HVAC, and lighting to reduce costs and carbon footprint without compromising output.
- Instant production insights Advanced analytics synthesize operational data into concise, actionable insights—delivered via dashboards, alerts, and automated recommendations—so managers can make informed decisions in real time.
Typical Activities Inside a Smart Factory
A smart factory’s daily operations illustrate how these capabilities come together:
- Robots perform repetitive and precision assembly tasks while adapting to variations in parts and cycle times.
- AI models forecast demand surges and recommend schedule adjustments or inventory shifts to meet changing orders.
- Autonomous forklifts and guided vehicles transport materials efficiently, reducing manual handling and transit delays.
- Computer vision systems inspect finished goods on the line, flagging defects and triggering immediate corrective actions.
- Live dashboards display key performance indicators—throughput, yield, downtime, and energy use—so teams can respond quickly to trends.
Real-World Use Cases of AI in Manufacturing
AI is already reshaping the manufacturing landscape across multiple industries. From automotive plants to pharmaceutical labs, AI-driven systems are improving accuracy, speed, and decision-making while reducing operational risks. Below are some of the most impactful real-world applications by sector.
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector has been one of the earliest and most aggressive adopters of AI. Factories now rely on AI-powered automation to increase precision and efficiency during vehicle production.
Key Applications:
- AI-powered robotic arms assemble vehicle components with high accuracy, ensuring consistent build quality.
- Computer vision systems detect welding imperfections, paint inconsistencies, and alignment errors in real time.
- Predictive analytics platforms monitor engine testing data to identify potential failures before vehicles reach the market.
AI helps manufacturers reduce production errors, streamline assembly, and improve end-to-end vehicle reliability.
Electronics Manufacturing
Electronics production requires microscopic precision, making AI a critical tool for ensuring flawless assembly.
Key Applications:
- AI-driven computer vision detects micro-level defects in semiconductors, circuit boards, and delicate components.
- Automated PCB (Printed Circuit Board) assembly systems use AI to accurately place and solder components.
- Smart IoT sensors monitor high-precision equipment, ensuring stability, accuracy, and consistent performance.
This leads to higher-quality electronics and reduced rates of product failure.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Pharmaceutical companies depend on AI to maintain compliance, improve safety, and ensure product integrity throughout production.
Key Applications:
- AI-based quality control systems ensure medicines meet strict regulatory standards at every step.
- Automated packaging and labeling systems eliminate human errors and maintain high hygiene standards.
- Demand forecasting algorithms analyze global data to optimize production and prevent medicine shortages.
AI helps the industry improve accuracy, speed, and global supply chain coordination.
Food & Beverage Industry
In food processing plants, AI plays a major role in ensuring hygiene, consistency, and efficient operations.
Key Applications:
- AI-powered inspection systems monitor hygiene and quality, identifying contaminants or packaging defects.
- Automated sorting, cutting, and packing machines enhance production speed and reduce waste.
- Advanced forecasting models predict demand and optimize inventory to prevent spoilage and overstocking.
These technologies create safer food products and more responsive supply chains.
Metal & Heavy Engineering
In heavy industries, AI enables safer and more reliable operations by handling massive machinery and high-risk environments.
Key Applications:
- Predictive maintenance tools track machine health and prevent failures in high-value industrial equipment.
- Autonomous material-handling systems transport heavy loads safely and efficiently across factory floors.
- Computer vision systems inspect metal structures for cracks, corrosion, and wear that are difficult to detect manually.
AI ensures enhanced safety, longer equipment life, and more consistent production quality.
Challenges in Implementing AI in Manufacturing
Implementing artificial intelligence in manufacturing delivers substantial operational gains, but it also introduces a set of practical, financial, and organizational challenges. The following sections expand on the most common obstacles manufacturers encounter and offer a concise view of their implications.
1. High Initial Investment
Adopting AI requires significant upfront capital for hardware, software, and infrastructure. Costs typically include sensors and edge devices, industrial-grade networking, cloud or on‑premise compute resources, AI platforms, and often new robotic systems. Beyond equipment, there are expenses for pilot projects, system integration, and change management. For many organizations, careful financial planning and phased rollouts are essential to manage cash flow and demonstrate early return on investment.
2. Skills Gap
Successful AI deployment depends on people who can design, operate, and maintain intelligent systems. Many manufacturing teams lack expertise in data science, machine learning, industrial automation, and IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things). Closing this gap requires targeted hiring, upskilling existing staff, and partnering with external specialists or integrators. Investing in training programs and cross‑functional teams helps ensure that AI tools are used effectively and sustainably.
3. Data Quality Issues
AI models are only as reliable as the data that feeds them. In manufacturing environments, data can be noisy, incomplete, inconsistent, or siloed across disparate systems. Poor data quality undermines model accuracy and can lead to false positives or missed anomalies. Addressing this challenge involves establishing robust data governance, standardizing data formats, implementing automated cleansing pipelines, and ensuring consistent sensor calibration and maintenance.
4. Integration with Legacy Systems
Many factories operate legacy equipment that was not designed for connectivity or modern control interfaces. Integrating AI with older PLCs, proprietary controllers, and bespoke software can be technically complex and costly. Solutions often require retrofitting sensors, deploying protocol converters, or building middleware to bridge old and new systems. A pragmatic approach combines targeted retrofits for high‑value assets with gradual modernization plans to minimize disruption.
5. Cybersecurity Risks
Connecting machines, sensors, and enterprise systems increases the attack surface and exposes operations to cyber threats. Vulnerabilities can lead to data theft, production disruption, or safety incidents. Effective mitigation requires a layered security strategy: network segmentation, secure device provisioning, encryption, continuous monitoring, and incident response planning. Security must be integrated into AI projects from the outset rather than treated as an afterthought.
Future of AI in Manufacturing (2026–2035)
AI will dramatically reshape the manufacturing landscape over the next decade. Key future developments include:
A. Fully Autonomous Factories
- Machines will self-monitor, self-adjust, and self-repair.
- Production lines will optimize themselves in real time.
- Minimal human intervention will be required for routine operations.
B. Hyper-Personalized Manufacturing
- AI will enable large-scale customization without increasing production cost.
- Products will be tailored to individual customer needs.
- Mass personalization will become a standard manufacturing model.
C. Voice-Controlled Factory Operations
- Supervisors will manage equipment using AI-powered voice assistants.
- Voice commands will simplify machine control, reporting, and workflow adjustments.
- Reduced training time and improved operational accessibility.
D. Multi-Robot Collaboration
- Robots will communicate and coordinate tasks with one another.
- AI will create teams of collaborative robots working like human crews.
- Enhanced efficiency, precision, and workload distribution.
E. Zero-Defect Manufacturing
- Advanced machine learning and computer vision will eliminate defects.
- Issues will be detected and resolved instantly during production.
- Consistent, high-quality output across all product batches.
F. Carbon-Neutral Smart Factories
- AI will optimize energy usage and reduce environmental waste.
- Smart systems will track emissions and improve sustainability.
- Future factories will aim for fully carbon-neutral operations.
Will AI Replace Human Workers
No. Artificial intelligence is a powerful tool that augments human capabilities rather than rendering people obsolete. In practice, AI takes on specific types of work while humans retain roles that require judgment, creativity, and leadership.
Tasks Best Handled by AI
AI excels at activities that are repetitive, hazardous, or heavily data‑driven. Typical responsibilities where AI adds the most value include:
- Repetitive tasks such as routine assembly, data entry, and standardized inspections.
- Hazardous jobs that expose people to risk, including handling toxic materials or operating in dangerous environments.
- Data‑heavy analysis where large volumes of sensor, production, or market data must be processed quickly to reveal patterns.
- Automated quality inspection using computer vision and pattern recognition to detect defects at scale.
- Continuous machine monitoring for predictive maintenance and real‑time anomaly detection.
By taking on these functions, AI improves safety, consistency, and throughput while freeing human workers for higher‑value activities.
Roles That Remain Human‑Centric
There are core areas where human skills are essential and difficult to automate. These include:
- Creativity — generating novel ideas, designing new products, and imagining alternative futures.
- Complex decision‑making — weighing ambiguous tradeoffs, interpreting ethical considerations, and making strategic choices.
- Problem‑solving — diagnosing novel issues, synthesizing cross‑domain knowledge, and inventing workarounds.
- Supervision and people management — motivating teams, resolving conflicts, and mentoring talent.
- Innovation — driving organizational change, envisioning new business models, and translating insights into action.
These human strengths complement AI’s computational power and are central to long‑term competitiveness.
Final Thoughts
AI in manufacturing is not just an upgrade—it’s a complete transformation. Factories that embrace AI gain higher efficiency, reduced costs, better quality, and faster production. From predictive maintenance to intelligent robotics, AI empowers modern factories to operate smarter than ever before.
The manufacturers leading the next decade will be the ones who adopt AI today. Whether you run a small factory or a large industrial operation, AI-driven automation is the key to future-proofing your business.
FAQs
1. What is AI in manufacturing and why is it important?
Answer: AI in manufacturing refers to the use of artificial-intelligence tools — such as machine learning, computer vision, robotics, and predictive analytics — to automate tasks, improve efficiency, enhance quality control, and reduce costs. It is important because it enables factories to operate faster, smarter, and with fewer errors than traditional methods.
2. How does AI help reduce downtime in factories?
Answer: Through predictive maintenance and real-time equipment monitoring, AI analyzes data from sensors (like temperature, vibration, pressure) to forecast machine failures before they occur. This lets manufacturers perform maintenance proactively — reducing unexpected breakdowns and keeping production lines running smoothly.
3. Can AI improve product quality in manufacturing?
Answer: Yes. AI-driven systems — such as computer vision for defect detection or automated inspection tools — can identify flaws (surface defects, shape deviations, structural errors) faster and more accurately than manual inspection. This ensures higher consistency, reduces waste, and improves final product reliability.
4. Will AI replace human workers in manufacturing?
Answer: No. While AI excels at repetitive, data-intensive, or hazardous tasks, human workers remain essential for creativity, complex decision-making, problem-solving, oversight, and innovation. The future lies in collaboration — AI supporting humans, not replacing them.
5. What industries benefit most from AI-driven manufacturing automation?
Answer: Industries that demand high precision, volume, safety, or speed benefit greatly. This includes automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, and heavy-engineering sectors. AI-driven automation helps these industries reduce costs, improve quality, boost productivity, and scale operations more efficiently.