Multimodal AI systems are advanced models that can process and understand multiple types of data—such as images, text, audio, video, and sensor inputs – at the same time. Unlike traditional AI, which focuses on a single input type, multimodal AI learns by combining different sources of information, enabling it to understand context more deeply, make more accurate decisions, and interact more naturally with humans.
These systems “see” through computer vision, “hear” using speech recognition, “read” via natural language understanding, and “reason” by merging all these inputs into one unified understanding. In simple terms: multimodal AI brings together all senses of intelligence – similar to how humans learn and understand the world.
What Are Multimodal AI Systems?
Multimodal AI systems are artificial intelligence models designed to understand and interpret data from different modalities. A modality refers to a type of input format—such as:
- Visual data: images, graphics, videos
- Audio data: speech, music, environmental sounds
- Text data: documents, articles, instructions
- Sensor data: motion, depth, temperature, and more
When these inputs are processed together, AI gains a richer, more complete understanding of the world around it.
Why Multimodal Matters
Humans rarely use only one sense to understand something. We use sight, sound, and context together. Multimodal AI attempts to replicate this, making technology smarter, more aligned with real-world environments, and capable of more natural interactions.
How Multimodal AI Works: The Simple Explanation
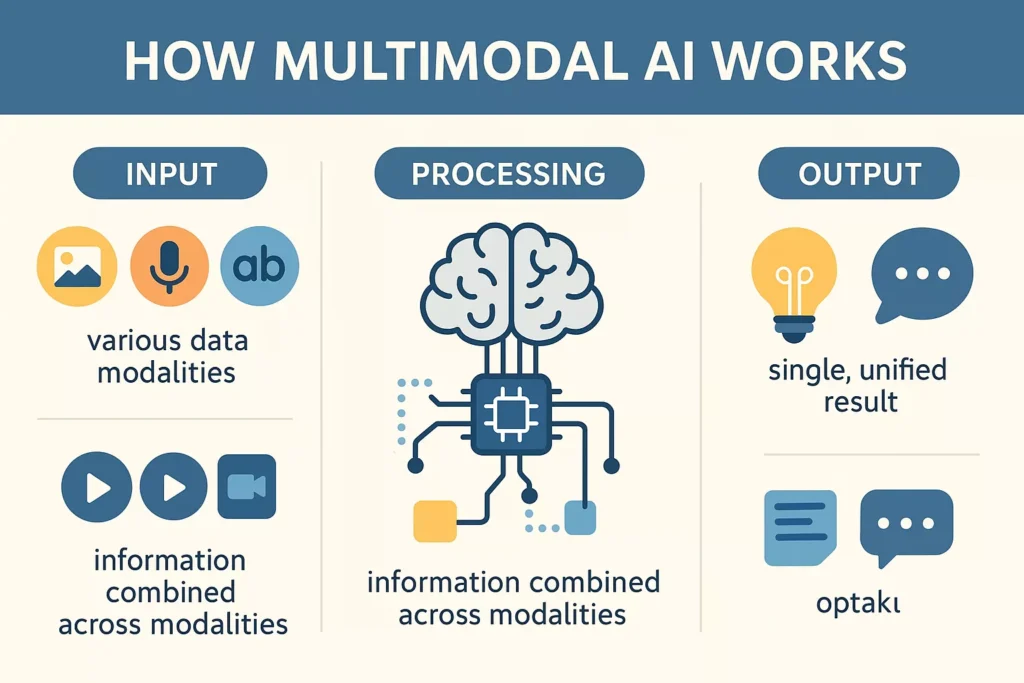
Multimodal AI works through a unified architecture that merges different data types into one shared representation. The model then uses this combined representation to generate outputs—text, classifications, predictions, or even images.
Core Working Steps:
- Input Collection
The system receives data across multiple channels—images, audio, and text. - Feature Extraction
Specialized models like CNNs (for images) or Transformers (for text) process individual data types. - Fusion Layer
The extracted information is merged. This is where the “understanding together” part actually happens. - Reasoning & Decision-Making
The model identifies patterns, relationships, and meaning across all modalities. - Output Generation
The system produces results such as answers, descriptions, decisions, or new content.
Key Capabilities of Multimodal AI Systems
1. They See
Through advanced computer vision, multimodal models can:
- Recognize objects
- Detect faces
- Identify actions in videos
- Understand visual scenes
- Interpret graphs, charts, and diagrams
This “seeing” capability becomes even stronger when paired with text or audio interpretations.
2. They Hear
Multimodal AI systems include built-in audio interpretation skills like:
- Speech-to-text
- Noise classification
- Emotion recognition
- Speaker identity detection
- Audio event prediction
This allows them to understand tone, context, and commands with higher accuracy.
3. They Read
Natural Language Processing (NLP) powers the reading ability:
- Understanding written documents
- Extracting meaning from text
- Summarizing content
- Translating languages
- Interpreting instructions
When these reading skills combine with vision and audio, the system becomes significantly more powerful.
4. They Understand Together
This is what truly sets multimodal AI apart.
The system blends all forms of input and reaches a deeper, more contextual understanding. For example:
- A video of a person talking can be interpreted using facial movements (vision), voice tone (audio), and spoken words (text).
- A picture of a restaurant combined with reviews helps AI judge whether the place is romantic, family-friendly, or popular.
- Audio-based emotion detection plus text analysis improves customer service bots.
The power lies in fusion—not separate processing.
Why Multimodal AI Is Transforming the Future
1. Richer Context and Higher Accuracy
Single-model AI can miss details. Multimodal AI doesn’t.
Example:
A text-only model reading “The man dropped the ball” doesn’t know if it’s literal or metaphorical. But a multimodal model with video input does.
2. More Natural Human–AI Interaction
Humans communicate using:
- Voice
- Gestures
- Expressions
- Text
- Visual cues
Multimodal AI allows machines to respond naturally to these same signals.
3. Real-Time Decision Making
Industries like healthcare, robotics, and autonomous vehicles rely on rapid multimodal data interpretation to ensure accurate outcomes.
4. Better Reasoning & Reduced Ambiguity
When AI uses multiple sources of truth, misunderstandings reduce significantly.
Seeing + hearing + reading = fewer errors.
5. Unlocking New Applications
Multimodal AI is making previously impossible applications possible—such as AI tutors, realistic robots, advanced AR/VR, and highly intelligent assistants.
Real-World Applications of Multimodal AI
1. Healthcare
Multimodal AI improves diagnosis by analyzing:
- X-ray images
- Patient history
- Doctor notes
- Lab reports
It can detect diseases faster and more accurately.
2. Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars rely on:
- Cameras
- Lidar sensors
- Radar
- GPS signals
- Spoken instructions
Multimodal fusion ensures safer decision-making on the road.
3. Customer Service
AI support agents can:
- Read customer queries
- Understand customer tone through audio
- Analyze past messages
- Recommend solutions instantly
This creates highly personalized, emotion-aware support.
4. Education & Learning
AI tutors can:
- Read student handwriting
- Understand spoken questions
- Interpret expressions to detect confusion
- Tailor teaching methods
Learning becomes adaptive and engaging.
5. Security & Surveillance
Systems can monitor environments using:
- Video analysis
- Sound detection
- Text logs
- Behavioral patterns
This results in smarter threat detection.
6. Entertainment & Content Creation
Multimodal AI helps create:
- Realistic characters
- Voice-activated games
- AI-generated videos
- Virtual assistants
- Auto-captioned content
Creativity becomes more accessible for everyone.
7. Smart Devices & IoT
Household AI systems combine:
- Visual recognition
- Speech commands
- Sensor data
This enables smarter home automation and personalized assistance.
Multimodal vs. Unimodal AI: Clear Comparison
| Feature | Unimodal AI | Multimodal AI |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | One type (e.g., text only) | Multiple types combined |
| Accuracy | Limited | Higher |
| Reasoning | Lower | Strong contextual reasoning |
| Human Interaction | Less natural | Much more natural |
| Use Cases | Narrow | Wide and expanding |
| Adaptability | Restricted | Extremely flexible |
Multimodal AI clearly outperforms traditional unimodal systems in almost every dimension.
How Multimodal AI Models Are Trained
Training multimodal AI requires:
- Large paired datasets (image+text, audio+transcripts, etc.)
- Pre-trained models for each modality
- Fusion layers to combine signals
- Alignment techniques to connect meaning across domains
Modern architectures like CLIP, Gemini, GPT-4/5, LLaVA, and Flamingo lead this field.
Benefits of Multimodal AI for Businesses
1. Enhanced Customer Experience
Multimodal AI allows businesses to understand customers on a deeper, more human level. Instead of relying only on text inputs, these systems analyze voice tone, facial expressions, sentiment, and past interactions to deliver more personalized responses. For example, a customer support bot powered by multimodal AI can detect frustration in a caller’s voice, read their previous messages for context, and analyze order history simultaneously—leading to faster resolutions and improved customer satisfaction. This level of intelligence helps brands build stronger, more empathetic relationships with users.
2. Better Insights From Complex Data
Modern businesses handle enormous volumes of data that come in many formats—documents, audio notes, security video feeds, charts, and more. Multimodal AI can process and merge all these data types, turning them into clear, actionable insights. In healthcare, it can combine medical scans, patient histories, and doctor notes to support accurate diagnoses. In security, it can analyze video footage alongside access logs to detect unusual patterns. This holistic view allows organizations to make more informed decisions backed by complete, multi-source information.
3. Higher Engagement Across Marketing & Content
With the ability to analyze text, images, videos, and audio together, multimodal AI helps brands create more relevant, eye-catching content. Marketing teams can generate campaign visuals that match brand tone, analyze audience reactions from comments and facial expressions, and craft messages tailored to user preferences. This results in richer storytelling, more interactive ads, and highly targeted content that resonates better with viewers. The outcome is stronger engagement, higher conversion rates, and a more memorable brand presence.
4. Cost Efficiency Through Smarter Automation
Multimodal AI significantly reduces operational costs by improving automation reliability and reducing the need for human input in repetitive processes. It can automatically review documents, analyze videos for compliance, classify customer feedback, and handle voice-based tasks simultaneously. Because it understands multiple data types at once, it minimizes errors and reduces the time spent on manual reviews, approvals, or monitoring. This streamlined workflow allows businesses to scale operations while saving resources.
5. Competitive Advantage & Faster Decision-Making
Companies embracing multimodal AI gain a major edge in speed, innovation, and accuracy. They can respond to market trends faster, detect issues earlier, and make decisions supported by real-time visual, audio, and textual insights. Whether it’s an e-commerce company dissecting customer behavior or a financial firm analyzing market signals, multimodal AI turns data into strategic power. The result is smarter operations, enhanced productivity, and an ability to outperform competitors who rely on traditional, single-channel AI systems.
Challenges of Multimodal AI Systems
Even though multimodal AI delivers exceptional capabilities, it also comes with significant challenges that businesses, developers, and researchers must address to ensure safe, efficient, and responsible deployment.
I. Data Alignment Complexity
One of the biggest barriers in multimodal AI is aligning different types of data so they carry the same meaning. Images must match their descriptions, audio must connect accurately with transcripts, and sensor readings must sync with real-world events. This process—called multimodal alignment—is extremely difficult because each data type has a different structure, noise level, and context. If alignment is off, the model may interpret the situation incorrectly, leading to unreliable results. Ensuring high-quality, perfectly paired datasets remains a major challenge.
II. High Computational Requirements
Multimodal models process enormous amounts of information—video frames, audio waves, text sequences, and sensor logs—all at once. This requires powerful GPUs, high memory, and large-scale training infrastructure. Small companies often find these requirements too expensive, making multimodal AI accessible mostly to large enterprises or research labs. Even after deployment, running these models in real time can be resource-intensive, increasing operational costs and limiting scalability.
III. Data Privacy Concerns
Multimodal AI often relies on sensitive inputs such as video footage, voice recordings, and personal documents. Handling such data introduces serious privacy risks. Video can reveal personal identities, audio can capture private conversations, and text may contain confidential information. Companies must follow strict data protection laws, implement encryption, reduce data retention, and ensure transparent usage policies. Mismanagement could lead to privacy breaches, legal consequences, and user distrust.
IV. Model Bias Amplification
Bias in AI can arise when training data is unbalanced or non-representative. In multimodal systems, the problem becomes even more complex. Bias can enter through text datasets, image collections, facial recognition samples, or audio sources—and when combined, these biases can reinforce one another. This may lead to unfair outputs, misclassification of certain groups, or inaccurate decision-making. Ensuring fairness requires continuous monitoring, bias evaluation, and diverse, well-curated datasets.
V. Explainability Issues
Understanding why a multimodal AI system arrived at a particular decision is still a major challenge. Since these models combine vision, audio, text, and other inputs, tracing which modality influenced the final output is difficult. This “black-box” problem makes auditing and debugging complex, especially in sensitive fields like healthcare or finance. Researchers are working on explainable AI (XAI) techniques, but full transparency for multimodal models is still in early stages.
Future of Multimodal AI
- Fully Integrated Digital Assistants
Future assistants will not just respond to text or voice—they will observe your environment through cameras, understand gestures, read documents, interpret emotions, and respond in the most natural, human-like way. These assistants will handle complex tasks such as coordinating schedules, analyzing visual data, summarizing conversations, and even predicting user needs before being asked.
- Context-Aware Robots
Multimodal AI will enable robots to navigate and interact with real environments more intelligently. They will combine visual cues, sound recognition, touch feedback, and spoken instructions to understand context, adapt to unexpected situations, and make autonomous decisions. This will revolutionize industries such as manufacturing, logistics, eldercare, and home automation.
- Smart AR/VR Environments
Immersive technologies will become far more interactive and realistic. Using multimodal understanding, AR/VR systems will track hand movements, interpret voice commands, analyze surroundings, and react instantly within virtual spaces. This will transform gaming, remote work, training simulations, virtual shopping, and digital learning into more immersive experiences.
- Emotionally Intelligent Systems
AI will interpret human emotions through tone of voice, facial expressions, body language, and text sentiment. This will lead to more empathetic customer service bots, mental health support tools, emotion-aware tutors, and adaptive workplace assistants that respond to user moods and needs.
- Real-Time Devices That Understand the World Like Humans
Everyday devices—from smartphones to smart glasses to home appliances—will process visual, audio, and text signals simultaneously. This will allow them to understand their surroundings, recognize user intent, and offer context-aware assistance in real time, making technology more intuitive and less intrusive.
- A Blurred Line Between Human and Machine Intelligence
As multimodal AI becomes more capable, its ability to perceive and respond to the world will approach human-like understanding. Machines will interpret complex situations, hold meaningful conversations, and offer insights based on multiple sensory inputs. The distinction between human intelligence and AI-driven assistance will increasingly fade as systems grow more adaptive, perceptive, and seamlessly integrated into daily life.
Conclusion
Multimodal AI systems represent the next major leap in artificial intelligence. By combining vision, audio, text, and sensor data into one unified model, they unlock deeper understanding, more accurate decisions, and natural human-like interactions.
From healthcare and education to autonomous vehicles and advanced digital assistants, multimodal AI is shaping the future of intelligent technology. As these systems continue to evolve, they will redefine how humans and machines interact – bringing us closer to truly intelligent and context-aware systems.
